It’s been an unusually hot summer across much of the world, and an even hotter time for divergence and dispersion across financial markets.
For starters, developed market central banks are pivoting to rate cuts, but on widely varying schedules. The European Central Bank, Bank of Canada, Swiss National Bank, and Bank of England have all cut rates in recent months and will likely cut further in 2024. The U.S. Federal Reserve hasn’t cut yet but is expected to start soon, particularly given emerging signs of labor market weakness. Meanwhile, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) just raised interest rates in late July.
We anticipated this dispersion in our April 2024 Cyclical Outlook, “Diverging Markets, Diversified Portfolios.” We said the increasingly asynchronous paths of economic growth, inflation, and central bank policy among nations would create elevated volatility and attractive investment opportunities across global bond markets.
Lately, the divergence theme has been playing out in real time, extending beyond sovereign debt to affect credit markets and stocks as well. Some examples:
- An encouraging inflation report after successive disappointing ones caused Australian 2-year bonds to rally on 31 July. That same day, the Bank of Japan raised interest rates by 25 basis points (bps), and Japan 2-year yields rose. The moves produced an immediate 30-bp differentiation between Australian and Japanese front-end rates.
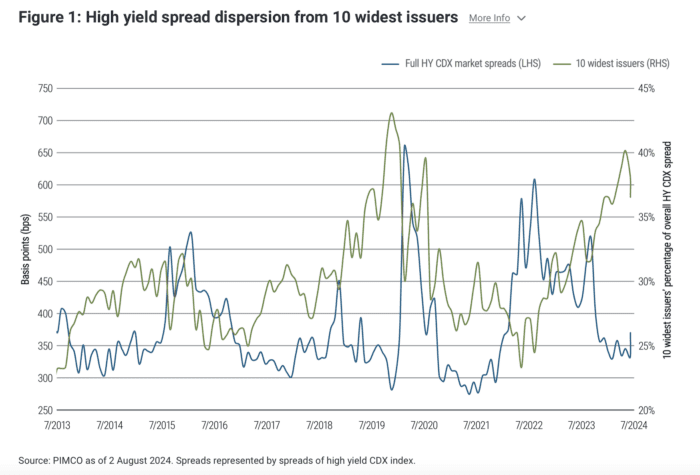
- Spread dispersion in the high yield CDX index is near all-time highs. As of 2 August, 37% of the overall credit spread of the widely followed market gauge came from the 10 constituent issuers trading at the widest spreads (see Figure 1), reflecting elevated default risk and depressed recovery prospects for the lowest-rated bonds. For much of the rest of the high yield market, spreads have been unusually tight.
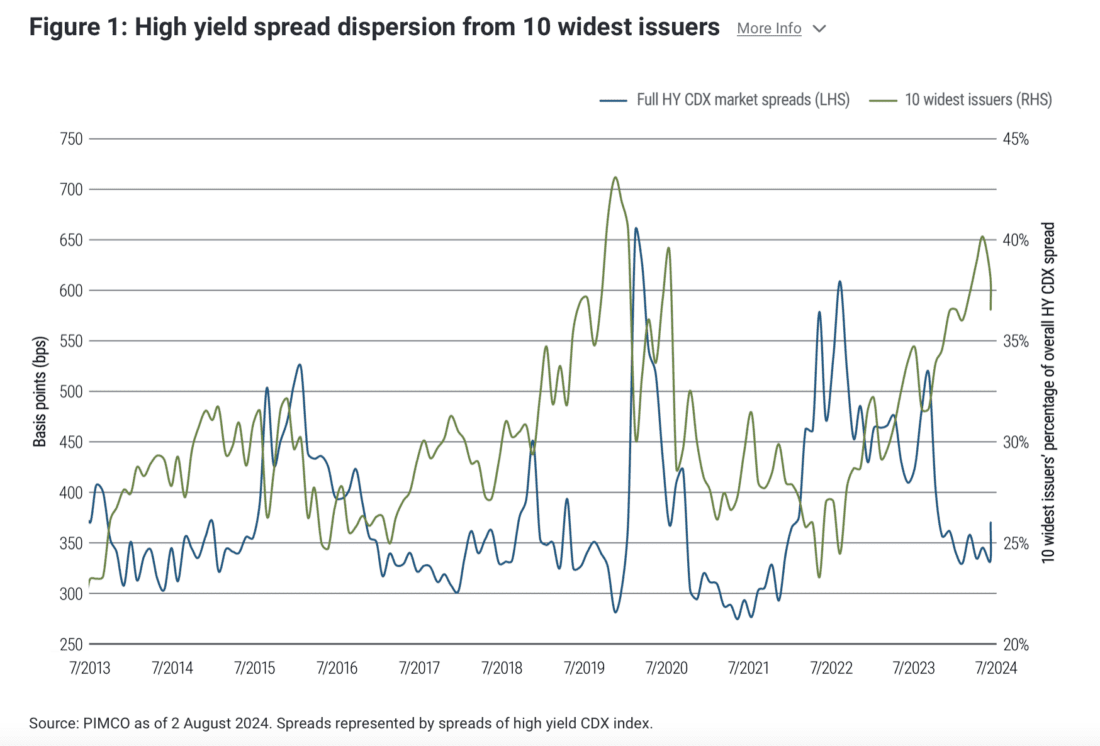
Past performance is not indicative of future results.
- The equity market has experienced outsize divergences between high-growth tech companies and small-cap stocks. Large tech stocks have tumbled lately due to lackluster earnings and concerns about returns on AI investment, while small caps have rallied. This rotation followed months of strong outperformance and crowded positioning in tech stocks. The Nasdaq 100 had outperformed the Russell 2000 by 21.7% in 2024 as of 10 July. Since then, the Russell has outperformed the Nasdaq by 13.6% as of 2 August, including a record 5.8% outperformance on 11 July.
- Stocks sold off and bonds surged in early August after a disappointing July jobs report rekindled U.S. recession fears that had seemed dormant for months. Not only dispersion but illiquidity is at play: For example, on 5 August, Japan’s Nikkei stock index fell a whopping 12.4%, putting it in negative territory for the year before recovering almost all those losses in the very next trading session.
We expect continued global volatility and dispersion as tight monetary policy and elevated sovereign debt levels threaten economic growth, particularly in a year of major elections in countries making up 60% of world GDP. Thankfully, this sort of volatility can create engaging trading opportunities for active investment managers.
The recent market swings have been a wake-up call for many investors who had enjoyed favorable returns in stocks and cash for much of this year. Back in May, we noted the potential benefits of extending duration and locking in attractive bond yields (see “The Cost of Cash: A $6 Trillion Question”). As we said then, “A yield decline of just about 80 bps has the potential to generate price appreciation and lead to a portfolio of short and intermediate maturities doubling the return of cash.” The 2-year Treasury yield has fallen by more than a full percentage point since then.
More economic risks ahead
Central banks did well to tame the post-pandemic inflation spike with coordinated interest rate hikes. Inflation across many regions rose to painful levels for a brief period, but it continues to retreat thanks in large part to policymakers’ quick actions. Rates have also remained relatively contained and have been on a downward path of late, providing a tailwind for bonds.
Signs of weakening in other developed economies had for months contrasted with resilient U.S. growth, but lately even the U.S. appears vulnerable.
The July jobs data reached the cusp of triggering the Sahm Rule, a Fed gauge (based on employment data) that in the past has been a reliable indicator of U.S. recession. It’s worth noting that this rule has historically been triggered when actual levels of employment are declining, which hasn’t happened in a material way yet – recent weakness has more to do with labor supply as increasing numbers of job seekers enter the market (see Figure 2).

Still, labor market strain could warrant an accelerated pace of rate cuts once the Fed starts easing policy. That would be consistent with prior cycles. Since the 1980s, when the Fed was hiking, only 25% of those hikes were by increments of more than 25 bps. By contrast, when the Fed cut, it did so by increments greater than 25 bps about half of the time. History also shows forecasters regularly tend to underestimate how aggressively central banks cut rates.
Amid this incipient policy divergence, we find bonds in countries such as the U.K., Canada, and Australia attractive due to downside economic growth risks, an improving inflation outlook, and how interest rates more directly affect the economy there through home mortgage structures. We also like trades that position for potential outcomes of this global dispersion, such as steeper yield curves in the U.S. versus flatter ones in Japan.
The recent market swings also serve as a reminder of the hedging properties of bonds, which tend to shine in these conditions. The diversification offered by an actively managed global bond allocation can serve as broad-based ballast, generating the potential for attractive income and capital appreciation, particularly in volatile times. Think of a bond fund allocation as an attractive option to help keep portfolios cool and comfortable on a hot summer day.
—
Originally Posted August 6, 2024 – Summer of Dispersion
Disclosure: PIMCO
All investments contain risk and may lose value. This material is intended for informational purposes only. Forecasts, estimates and certain information contained herein are based upon proprietary research and should not be considered as investment advice or a recommendation of any particular security, strategy or investment product. No part of this material may be reproduced in any form, or referred to in any other publication, without express written permission. PIMCO is a trademark of Allianz Asset Management of America L.P. in the United States and throughout the world. THE NEW NEUTRAL is a trademark of Pacific Investment Management Company LLC in the United States and throughout the world. ©2023, PIMCO.
Disclosure: Interactive Brokers Third Party
Information posted on IBKR Campus that is provided by third-parties does NOT constitute a recommendation that you should contract for the services of that third party. Third-party participants who contribute to IBKR Campus are independent of Interactive Brokers and Interactive Brokers does not make any representations or warranties concerning the services offered, their past or future performance, or the accuracy of the information provided by the third party. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
This material is from PIMCO and is being posted with its permission. The views expressed in this material are solely those of the author and/or PIMCO and Interactive Brokers is not endorsing or recommending any investment or trading discussed in the material. This material is not and should not be construed as an offer to buy or sell any security. It should not be construed as research or investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security or commodity. This material does not and is not intended to take into account the particular financial conditions, investment objectives or requirements of individual customers. Before acting on this material, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, as necessary, seek professional advice.
Disclosure: Futures Trading
Futures are not suitable for all investors. The amount you may lose may be greater than your initial investment. Before trading futures, please read the CFTC Risk Disclosure. A copy and additional information are available at ibkr.com.
Disclosure: Forex
There is a substantial risk of loss in foreign exchange trading. The settlement date of foreign exchange trades can vary due to time zone differences and bank holidays. When trading across foreign exchange markets, this may necessitate borrowing funds to settle foreign exchange trades. The interest rate on borrowed funds must be considered when computing the cost of trades across multiple markets.
Disclosure: ETFs
Any discussion or mention of an ETF is not to be construed as recommendation, promotion or solicitation. All investors should review and consider associated investment risks, charges and expenses of the investment company or fund prior to investing. Before acting on this material, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, as necessary, seek professional advice.













Join The Conversation
For specific platform feedback and suggestions, please submit it directly to our team using these instructions.
If you have an account-specific question or concern, please reach out to Client Services.
We encourage you to look through our FAQs before posting. Your question may already be covered!