See Part I, Part II , Part III and Part IV to get started.
Example 2 – Binomially distributed population
In the previous example, we knew that the population is exponentially distributed with parameter λλ=0.25.
Now you might wonder what would happen to the sampling distribution if we had a population which followed some other distribution say, Binomial distribution for example.
Would the sampling distribution still resemble the normal distribution for large sample sizes as stated by the CLT?
Let’s test it out. The following represents our Binomially distributed population (recall that Binomial is a discrete distribution and hence we produce the probability mass function below):
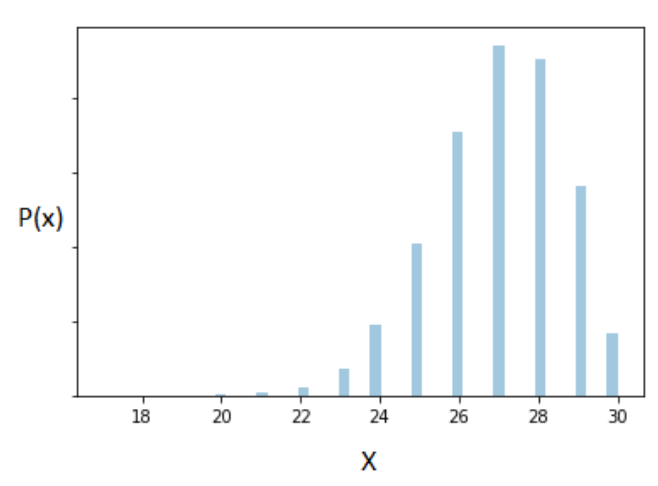

As before, we follow a similar approach and plot the sampling distribution obtained with a large sample size (n = 500) for a Binomially distributed variable with parameters k=30 and p = 0.9
# drawing 50 random samples of size 500 from a Binomial distribution with parameters k= 30 and p=0.9
sample_size=500
df500 = pd.DataFrame()
for i in range(1, 51):
exponential_sample = np.random.binomial(30,0.9, sample_size)
col = f’sample {i}’
df500[col] = exponential_sample
# Plotting the sampling distribution from a
df500_sample_means_binomial = pd.DataFrame(df500.mean(),columns=[‘Sample means’])
sns.distplot(df500_sample_means_binomial);
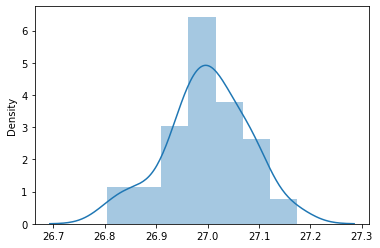
For this example, as we assumed that our population follows a Binomial distribution with parameters k = 30 and p =0.9, which means if CLT were to hold, the sampling distribution should be approximately normal with mean = population mean = μ=27μ=27 and standard deviation = σ/√nσ/n = 0.0734.
# Mean of sample means is close to the population mean
df500_sample_means_binomial.mean().values[0]
26.99175999999999
# Standard deviation of sample means is close to population standard deviation divided by square root of sample size
df500_sample_means_binomial.std().values[0]
0.06752975459086173
And the CLT holds again, as can be seen in the above plot.The sampling distribution for a Binomially distributed population also tends to a normal distribution with mean μ=μ= and standard deviation σ/√nσ/n for large sample size.
Stay tuned for the next installment, in which Ashutosh will go over an application of CLT in investing/trading.
Visit QuantInsti for additional details and to download full code: https://blog.quantinsti.com/central-limit-theorem/.
Disclaimer: All investments and trading in the stock market involve risk. Any decisions to place trades in the financial markets, including trading in stock or options or other financial instruments is a personal decision that should only be made after thorough research, including a personal risk and financial assessment and the engagement of professional assistance to the extent you believe necessary. The trading strategies or related information mentioned in this article is for informational purposes only.
Disclosure: Interactive Brokers Third Party
Information posted on IBKR Campus that is provided by third-parties does NOT constitute a recommendation that you should contract for the services of that third party. Third-party participants who contribute to IBKR Campus are independent of Interactive Brokers and Interactive Brokers does not make any representations or warranties concerning the services offered, their past or future performance, or the accuracy of the information provided by the third party. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
This material is from QuantInsti and is being posted with its permission. The views expressed in this material are solely those of the author and/or QuantInsti and Interactive Brokers is not endorsing or recommending any investment or trading discussed in the material. This material is not and should not be construed as an offer to buy or sell any security. It should not be construed as research or investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security or commodity. This material does not and is not intended to take into account the particular financial conditions, investment objectives or requirements of individual customers. Before acting on this material, you should consider whether it is suitable for your particular circumstances and, as necessary, seek professional advice.











Join The Conversation
For specific platform feedback and suggestions, please submit it directly to our team using these instructions.
If you have an account-specific question or concern, please reach out to Client Services.
We encourage you to look through our FAQs before posting. Your question may already be covered!