Margin Trading

What is Margin Trading?
There are two margin definitions. The term Securities margin is an alternative way to describe Security Financing and refers to borrowing money to purchase stock, bonds, or other financial instruments. However, commodities margin refers to the placement of cash (or in some cases, collateralizable assets) as a way to ensure the investor is able to handle most losses resulting from adverse movements in the price of the investments.
View InfographicBenefits of a Margin Trading Account
Use the cash or securities in your brokerage account as leverage to increase your buying power.
Get one of the best margin rates in the industry.1
Diversify trading strategies with short selling, options and futures contracts, or currency trading.
Borrow against a margin account at any time and repay the loan on your own schedule.
Understand the Risks of Margin Trading
Margin borrowing is only for experienced investors with high risk tolerance.
You may lose more than your initial investment.
Before trading on margin, understand the following risks
- Trading losses may be greater than the value of the initial investment
- Leveraged investments create a greater potential risk of loss
- Additional costs from margin interest charges
- Potential margin calls or liquidation of securities
How Trading Securities on Margin Works
Rules-based vs. Risk-based Margin
Margin models determine the type of brokerage accounts you open and the type of financial instruments you may trade. Trading on margin uses two key methodologies: rules-based and risk-based margin.
- In rules-based margin systems, your margin obligations are calculated by a defined formula and applied to each marginable product. This is the more common type of margin strategy used by securities traders.
- In risk-based margin systems, margin calculations are based on the risk inherent in your trading portfolio. The positions in your account are evaluated, including any hedged positions that decrease potential risk, and based on their risk profile, used to create your margin requirements.
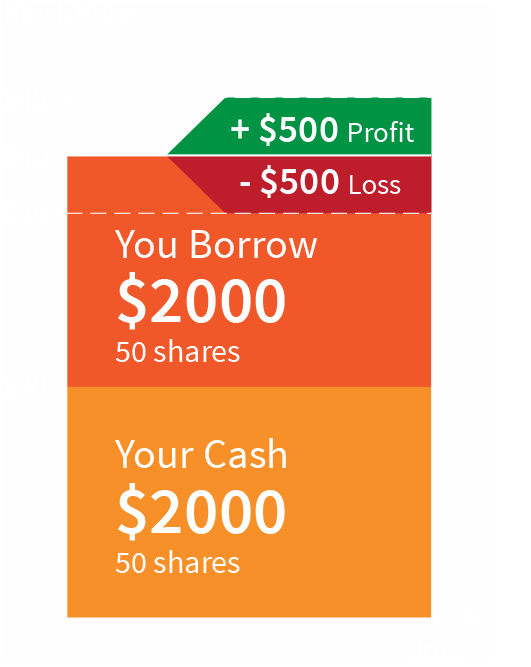
shares @ $40 (50 shares with cash and 50 shares on margin)
Rated Lowest Margin Fees1 by StockBrokers.com
US Margin Loan Rates Comparison2
| $ 25K | $ 300K | $ 1.5M | $ 3.5M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interactive Brokers | 5.14% | 4.81% | 4.59% | 4.48% |
| E-Trade | 11.95% | 10.45% | N/A | N/A |
| Fidelity | 11.33% | 10.08% | 7.50% | 7.50% |
| Schwab | 11.33% | 10.08% | N/A | N/A |
| Vanguard | 11.50% | 10.00% | N/A | N/A |
Each firm's information reflects the standard online margin loan rates obtained from their respective websites. Competitor rates and offers subject to change without notice. Services vary by firm.
Margin Education Course on Traders' Academy
Introduction to Margin Trading
This course is designed to help investors understand margin basics, including different types of margin accounts, margining methods, and margin requirements, plus how to monitor margin on both Trader Workstation (TWS) and IBKR Mobile.
Trading on margin is only for sophisticated traders. You may lose more than your initial investment.
- Introduction to Margin
- Monitoring Margin in Trader Workstation (TWS)
- Looking at Margin on IBKR Mobile


Start trading and investing like a professional today!
Open AccountDisclosures
- According to StockBrokers.com Interactive Brokers Review: Read the full article Online Broker Reviews, January 28, 2026. "The industry’s cost leader: Interactive Brokers continues to set the benchmark for cost efficiency, offering margin rates and high yields on idle cash that consistently outperform the competition."
- Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on USD margin loan balances for IBKR Pro as of February 4, 2026. Interactive Brokers calculates the interest charged on margin loans using the applicable rates for each interest rate tier listed on its website. Learn more about margin loan rates.
